When working with electrical panels, you might have come across terms like Neutral Bar and Ground Bar. But what exactly do they mean, and why should you care?
Understanding the difference between these two components is crucial for your safety and the proper functioning of your electrical system. You’ll discover clear explanations and practical tips that make these concepts easy to grasp. By the end, you’ll feel confident handling your electrical setup or communicating effectively with professionals.
Ready to clear up the confusion and protect your home or workspace? Let’s dive in.
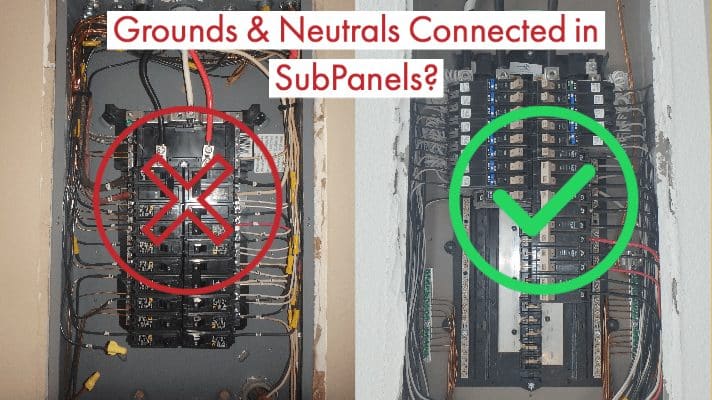
Credit: waypointinspection.com
Neutral Bar Basics
The neutral bar is a key part of electrical panels. It helps keep electrical systems safe and organized. Understanding its basics helps you know how electricity flows in your home or building.
Role In Electrical Panels
The neutral bar acts as a return path for electrical current. It balances the flow of electricity from live wires. Without it, circuits would not work properly. It also helps prevent electrical shocks and fires.
Connection And Function
The neutral bar connects all neutral wires in the panel. These wires carry current back to the power source. It ensures electricity completes its circuit safely. The bar keeps wires secure and tidy inside the panel.
Ground Bar Essentials
The ground bar is a key part of electrical panels. It keeps the system safe by directing extra electricity away. This helps protect people and devices from shocks and damage.
Understanding the ground bar helps you see why it is important in wiring systems. It also shows how it fits into the overall setup of electrical panels.
Purpose In Wiring Systems
The ground bar collects all ground wires in one spot. It sends unwanted electricity safely into the earth. This prevents electrical shocks and fires.
It connects metal parts of the system to the earth. This stops dangerous voltage from building up. The ground bar works quietly but is very important for safety.
Typical Placement And Setup
The ground bar is usually inside the main electrical panel. It sits near the neutral bar but is separate. Each ground wire is attached to the bar with screws.
It must be securely fastened to the panel. This ensures a solid path to the earth. Proper setup avoids loose connections that can cause hazards.
Electrical Differences
The electrical differences between a neutral bar and a ground bar are key to understanding their roles in an electrical panel. These differences affect how electricity flows and how safety is maintained. Knowing these basics helps in proper wiring and system design.
Voltage Levels Handled
The neutral bar carries current at a voltage close to zero, as it serves as a return path for electrical current. It connects to the neutral point of the power source and handles the voltage that returns from devices.
The ground bar usually carries no current during normal operation. It is connected to earth ground and helps protect people and equipment by safely directing fault current away. The voltage on the ground bar should be zero or near zero.
Current Flow Characteristics
The neutral bar carries current during normal circuit operation. It completes the electrical circuit by allowing current to return to the source. This current varies depending on the load connected.
The ground bar only carries current during a fault or short circuit. It acts as a safety path to prevent electric shock or damage. Normally, no current flows through the ground bar.
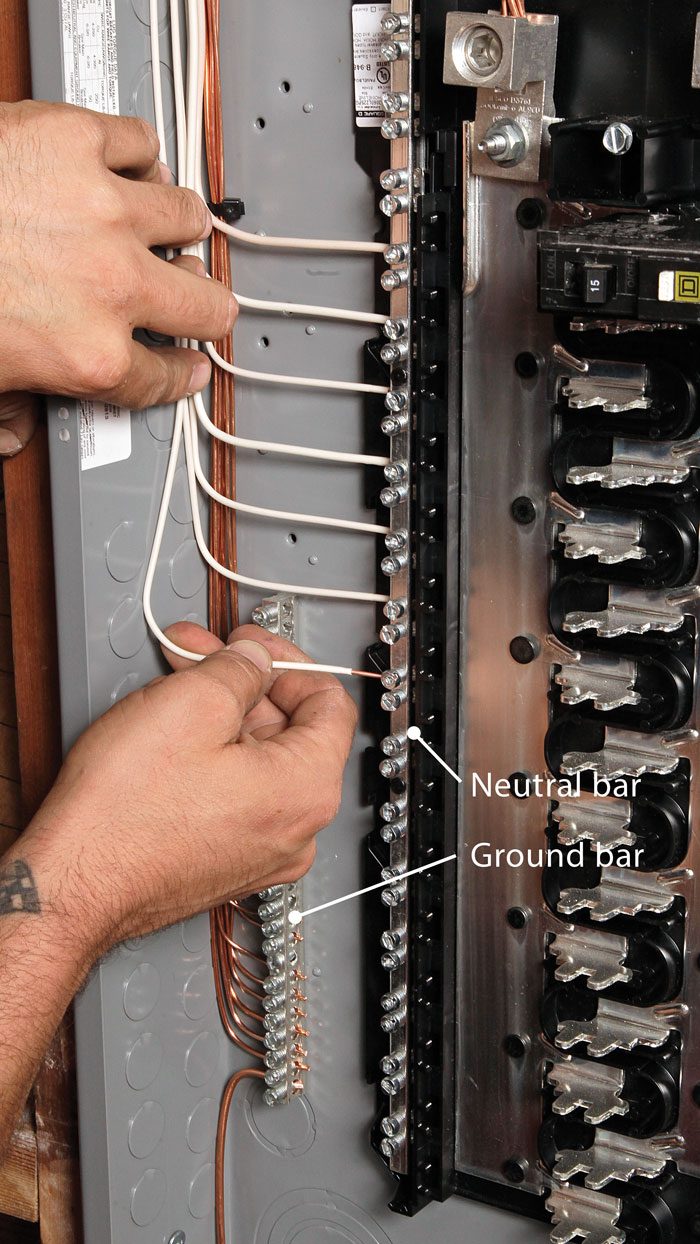
Credit: www.finehomebuilding.com
Safety Considerations
Safety is a key factor when choosing between a neutral bar and a ground bar. Both parts have distinct roles in electrical panels. Understanding their safety implications helps prevent accidents and electrical faults. Proper use of these components protects people and property from harm.
Keeping circuits safe means knowing the difference between neutral and ground bars. Mistakes in wiring can lead to shocks or fires. Careful installation and maintenance are essential to ensure safety in any electrical system.
Preventing Electrical Hazards
Neutral bars carry current during normal operation. Ground bars only carry current during faults. Mixing these can cause dangerous electrical shocks. Proper separation reduces the risk of short circuits and fires. Always connect wires to the correct bar. Regular checks help find loose or damaged connections early.
Code Compliance Requirements
Electrical codes require neutral and ground bars to be separate in most panels. This rule helps keep systems safe and reliable. Inspectors look for correct installation in homes and buildings. Following the rules avoids fines and costly repairs. Use approved parts and follow local electrical codes strictly.
Installation Practices
Proper installation of neutral bars and ground bars ensures electrical safety and system reliability. These components must be installed carefully to avoid hazards and maintain code compliance. Understanding key installation practices helps prevent common errors and supports a well-functioning electrical panel.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Mixing neutral and ground wires on the same bar can cause serious electrical issues. Do not connect grounding wires to the neutral bar beyond the main panel. Overcrowding wires on one bar reduces effective grounding and can cause overheating. Avoid using loose or damaged connectors that can lead to poor connections. Skipping the inspection of bar mounting tightness may result in vibration and wire loosening.
Best Practices For Setup
Install neutral and ground bars separately inside the panel. Use the correct size bar for the number of wires and panel type. Tighten all screws firmly to secure wires and bars. Label each bar clearly to avoid confusion during maintenance. Follow local electrical codes and manufacturer instructions precisely. Check for proper wire stripping and insertion to maintain solid contact.
Troubleshooting Tips
Troubleshooting issues with neutral bars and ground bars requires careful attention. Small mistakes can cause electrical problems or safety risks. Knowing how to spot faults and maintain connections is key. The tips below help keep your electrical system safe and working well.
Identifying Faulty Connections
Check for loose wires around the neutral and ground bars. Loose connections can cause sparks or power loss. Look for discoloration or burn marks on the bars. These signs often mean overheating or short circuits. Use a screwdriver to gently tighten all screws. Also, listen for buzzing sounds, which can signal poor contact. Test continuity with a multimeter to confirm proper connections.
Maintaining System Integrity
Keep the bars clean from dust and corrosion. Dirt can cause poor electrical contact and faults. Use a dry cloth or soft brush to clean the bars regularly. Avoid using water or chemicals that may cause damage. Inspect the bars for cracks or rust. Replace any damaged parts immediately to prevent hazards. Ensure wires are neatly organized and labeled to avoid confusion. Proper maintenance extends the life and safety of your system.
Choosing Between Neutral And Ground Bars
Choosing between neutral and ground bars is key in electrical panel design. Both bars serve different roles but work together for safety and function. Understanding their differences helps in making the right choice for your project.
Factors Influencing Selection
Material quality affects durability and conductivity. Copper bars offer better conductivity but cost more. Aluminum bars are cheaper but less efficient. Size of the electrical panel also matters. Larger panels need bars that handle more connections.
Safety standards guide the choice too. Electrical codes require specific bars for neutral and ground wires. Proper separation prevents electrical faults and hazards. Installation space can limit the type of bar used. Choose bars that fit well without crowding the panel.
Application Scenarios
Neutral bars are used to connect neutral wires from circuits. They carry current back to the power source. Ground bars connect grounding wires for safety. They provide a path for fault currents to the earth.
In residential panels, separate bars keep neutral and ground wires apart. In commercial panels, bars may be combined but require strict code compliance. Industrial settings often need robust bars to handle high currents. Selecting the right bar ensures system safety and reliability.

Credit: diy.stackexchange.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Function Of A Neutral Bar?
A neutral bar carries current back to the power source in an electrical panel.
How Does A Ground Bar Differ From A Neutral Bar?
A ground bar connects all grounding wires to protect against electrical faults.
Can Neutral And Ground Bars Be Combined In One Panel?
Yes, but only in certain panels and under specific electrical codes.
Why Is Grounding Important In Electrical Systems?
Grounding prevents shocks by safely directing electricity into the earth.
Where Are Neutral And Ground Bars Typically Installed?
They are installed inside electrical distribution panels or breaker boxes.
What Materials Are Used For Neutral And Ground Bars?
Usually, copper or aluminum is used for good electrical conductivity.
Conclusion
Neutral bars and ground bars serve different safety roles in electrical systems. The neutral bar carries return current, while the ground bar handles fault current. Both must be installed correctly to keep systems safe and working well. Knowing their functions helps avoid wiring mistakes and electrical problems.
Proper use of neutral and ground bars protects people and equipment from shocks and damage. Always follow electrical codes and guidelines when working with these bars. Clear understanding makes electrical work safer and more reliable.
