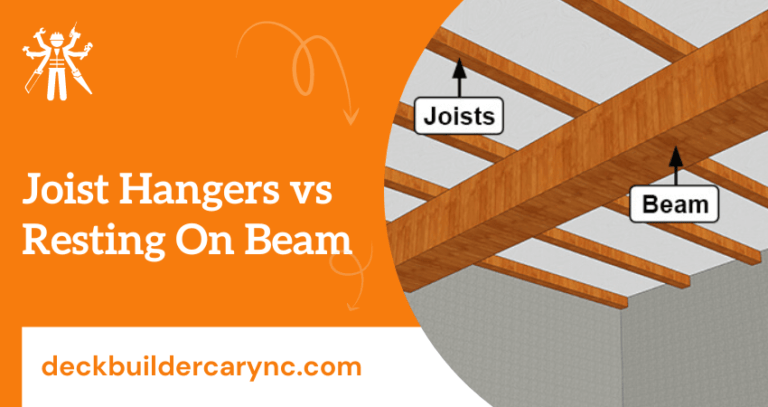
When building or renovating your home, choosing the right support for your floor joists can make all the difference. You might be wondering: should your joists rest directly on a beam, or should you use joist hangers to hold them in place?
This decision affects not only the strength and stability of your structure but also how long it will last and how safe it will be for you and your family. You’ll discover the key differences between joist hangers and resting joists on beams, helping you make the best choice for your project.
Keep reading to find out which method suits your needs and ensures your home stands strong for years to come.
Joist Hangers Basics
Joist hangers are metal brackets used to support wood beams in construction. They hold the joists in place and keep the structure strong. Choosing the right joist hanger is important for safety and durability. Understanding the basics helps you compare joist hangers with resting joists on beams.
Joist hangers provide a secure connection between beams and joists. They prevent movement and reduce stress on wood joints. This makes them a popular choice in many building projects.
Types Of Joist Hangers
There are several types of joist hangers for different needs. Face mount hangers attach to the side of a beam. Top mount hangers sit on top of the beam. These types help fit joists at various angles. Specialty hangers are made for unique framing situations. Choosing the right type depends on your project’s design.
Materials Used
Most joist hangers are made from steel for strength. Steel can resist heavy loads and last for years. Galvanized steel is common because it resists rust and corrosion. Some hangers use stainless steel for extra durability. The material must match the environment to avoid damage over time.
Installation Techniques
Installing joist hangers correctly is key for safety. Use nails or screws made for structural use. Fasteners must fit the hanger holes properly. The hanger should sit flush against the beam and joist. Check alignment before securing all fasteners. Proper installation prevents joists from shifting or falling.

Credit: positive.ie
Resting Joists On Beams
Resting joists on beams is a traditional way to support floors or decks. This method places the joists directly onto the beam, which carries the weight. It is simple and effective for many building projects. Understanding how this works helps in choosing the right support for your structure.
Common Methods
One common method is to notch the beam so the joist fits securely. Another way is to use metal hangers for extra support. Sometimes, joists rest on a ledger board attached to the beam. These methods keep the joists stable and prevent movement.
Load Distribution
Resting joists on beams spreads the weight evenly along the beam. The beam then transfers the load to the posts or walls below. Proper load distribution prevents sagging or damage to the structure. This keeps floors strong and safe over time.
Beam Selection
Choosing the right beam depends on the load and span length. Larger spans need stronger, thicker beams. Wood species and grade also affect beam strength. Picking the correct beam helps support the joists and the entire structure properly.
Strength Comparison
Comparing the strength of joist hangers and resting joists on beams is important. Strength affects safety and the lifespan of a structure. Both methods support joists but differ in how they carry loads and resist forces. Understanding these differences helps choose the best option for building projects.
Load Capacity
Joist hangers provide direct support by wrapping around the joist ends. This allows them to hold more weight evenly. Resting joists on beams relies on the beam’s surface area to carry the load. Joist hangers often have higher load capacity due to metal reinforcement. Resting joists may risk shifting under heavy loads.
Durability Factors
Joist hangers are made from strong steel, offering long-term durability. They resist bending and warping better than wood alone. Resting joists depend on the beam’s wood condition, which can weaken over time. Metal hangers maintain their shape and strength under stress. Wood beams need regular checks for cracks or rot.
Resistance To Environmental Stress
Joist hangers often come with coatings that protect from rust and corrosion. This makes them suitable for outdoor or damp areas. Resting joists on beams expose wood to moisture and insects. Wood can swell, shrink, or decay due to weather changes. Metal hangers provide a more stable, weather-resistant connection over time.
Credit: deckbuildercarync.com
Installation Challenges
Installing joist hangers versus resting joists on beams presents unique challenges. Each method requires careful attention to detail. Mistakes can weaken the structure or cause delays. Understanding common problems and necessary tools helps avoid trouble.
Common Mistakes
Incorrect placement of joist hangers causes weak support. Nails or screws that are too short reduce strength. Resting joists without proper alignment leads to uneven floors. Skipping measurements results in gaps or overcrowding. Overlooking manufacturer instructions often causes installation errors.
Tools And Equipment
Joist hangers need specific tools like a hammer, nails, and a level. Power drills and impact drivers speed up fastening. Measuring tape and carpenter’s square ensure precise cuts. For resting joists, saws and chisels may be necessary to fit beams. Using the right tools improves safety and accuracy.
Time And Labor
Installing joist hangers takes more time than resting joists. Each hanger must be positioned and fastened carefully. Resting joists requires less hardware but more lifting and fitting. Both methods need physical effort and attention to detail. Planning labor helps finish the job efficiently.
Cost Implications
Cost plays a big role in choosing between joist hangers and resting joists on beams. Both methods affect your budget differently. Understanding these costs helps you make a smart choice for your project.
Material Costs
Joist hangers need metal brackets. These brackets add to your material expenses. Resting joists on beams requires larger beams. Larger beams may cost more wood. Metal hangers are usually cheaper than extra wood. Material choice impacts the overall price.
Labor Expenses
Installing joist hangers takes time and skill. Workers must place and nail each hanger carefully. This can increase labor costs. Resting joists on beams may require less precise work. It can reduce labor time and costs. Labor charges depend on the method used.
Long-term Maintenance
Joist hangers can corrode over time. Corrosion may lead to repairs or replacements. Resting joists on beams may need less maintenance. However, beams can suffer from rot or warping. Maintenance costs vary based on materials and environment.

Credit: forum.nachi.org
Safety Considerations
Safety is the top priority when choosing between joist hangers and resting joists on beams. Both methods affect the strength and stability of a structure. Understanding safety factors helps avoid costly repairs and accidents. Proper installation and maintenance keep your building secure.
Building Codes
Building codes set the minimum safety standards for joist installation. Codes often require joist hangers for strong connections. Resting joists on beams may need extra support or specific spacing. Following local codes ensures your structure passes inspections. Ignoring codes can lead to fines and unsafe conditions.
Inspection Tips
Regular inspections detect problems early. Check for rust or damage on joist hangers. Look for cracks or splits in the wood where joists rest on beams. Ensure hangers are properly nailed or screwed in place. Loose or missing fasteners reduce strength. Keep an eye on signs of water damage or rot.
Preventing Structural Failures
Joist hangers provide consistent support and reduce movement. Resting joists directly on beams can cause shifting over time. Use hangers to prevent joists from slipping or twisting. Reinforce connections with nails or screws as needed. Proper load distribution stops sagging and collapse risks.
Choosing The Right Method
Choosing the right method for joist support affects the strength and safety of your structure. Both joist hangers and resting on beams have benefits. Knowing which method fits your project ensures a better build. Consider the needs of the project, the environment, and your budget before deciding.
Project Requirements
Every project has unique needs. Joist hangers provide strong, secure connections. They work well when space is tight or precise alignment is needed. Resting joists on beams is simpler. It suits projects with larger beams or when ease of installation matters. Assess the weight and size of your joists. Choose the method that matches your design and load demands.
Environmental Conditions
Weather and environment impact your choice. Joist hangers resist moisture better when made of galvanized steel. They reduce wood contact with water, preventing rot. Resting joists on beams may expose wood to dampness. Use this method in dry or protected areas. Think about wind, rain, and humidity. Pick the support that lasts longest in your climate.
Budget Constraints
Costs vary between methods. Joist hangers add material and labor expenses. Installation requires more skill and time. Resting joists on beams often costs less. It needs fewer materials and less labor. Balance cost with durability and safety. Choose the option that fits your budget and project goals without cutting corners.
Case Studies
Examining real-world case studies helps to understand the differences between joist hangers and resting on beam methods. These examples show how each technique performs in various settings. Practical insights from projects give clear guidance on which method fits best.
Residential Applications
In many homes, joist hangers provide strong support for decks and floors. They allow for easy alignment and secure fastening. Resting joists directly on beams is common in older houses. This method often requires extra blocking to prevent movement. Homeowners choose hangers for durability and beam resting for simplicity.
Commercial Projects
Commercial buildings favor joist hangers for their load-bearing capacity. They help meet strict building codes and safety standards. Resting joists on beams occurs in warehouses and storage areas. This method offers faster installation but may limit load capacity. Project managers weigh costs and structural needs carefully.
Renovation Examples
During renovations, joist hangers simplify adding new floors or decks. They minimize damage to existing structures and ensure stability. Resting joists on beams suits projects with limited space or budget. However, this method might need extra maintenance. Contractors choose based on site conditions and client goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Joist Hanger And How Does It Work?
A joist hanger is a metal bracket that holds joists to beams securely. It prevents movement and adds support.
Can Joist Hangers Replace Resting Joists On Beams?
Joist hangers provide stronger, more stable support than resting joists directly on beams. They reduce wood damage.
What Are The Benefits Of Resting Joists On Beams?
Resting joists on beams is simple and quick. It requires less hardware and skill.
Are Joist Hangers Better For Outdoor Construction?
Yes, joist hangers resist weather damage and keep joists firmly attached outdoors.
How Do Joist Hangers Affect Beam And Joist Lifespan?
Joist hangers reduce wood wear and water damage, extending the life of beams and joists.
Is It Cheaper To Use Joist Hangers Or Rest Joists On Beams?
Resting joists on beams costs less but joist hangers offer better safety and durability.
Conclusion
Choosing between joist hangers and resting joists on beams affects your structure’s strength. Joist hangers offer strong support and keep joists stable. Resting joists on beams is simpler but may need extra care. Consider your project’s needs and budget before deciding.
Proper installation ensures safety and durability. Both methods have pros and cons to weigh carefully. Think about load, weather, and materials used. Solid support prevents future problems and costly repairs. Your choice shapes the lifespan of your deck or floor.
